What is Artificial Intelligence and why it is useful for businesses
Innovation
Technology
Consulting
Home » What is Artificial Intelligence and why it is useful for businesses

What is Artificial Intelligence
Its evolution has been driven by key figures who have helped develop new learning techniques and create innovative applications in different fields. Today, AI has a significant impact on society and the economy, and its future will be determined by our ability to address the ethical and social challenges it poses.
How AI was born
In the early years of AI development, many researchers were optimistic about its potential and believed that intelligent machines could be created in a relatively short time. In 1956, U.S. mathematician and computer scientist John McCarthy coined the term “Artificial Intelligence” during the Dartmouth Conference, an event that gathered leading experts in the field and is considered the starting point of modern AI.
Between the 1950s and 1960s, AI experienced rapid growth thanks to advances in neural networks and machine learning. Key figures from this period include Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert, who founded the MIT AI Lab, a research center still recognized today as a leader in the field.
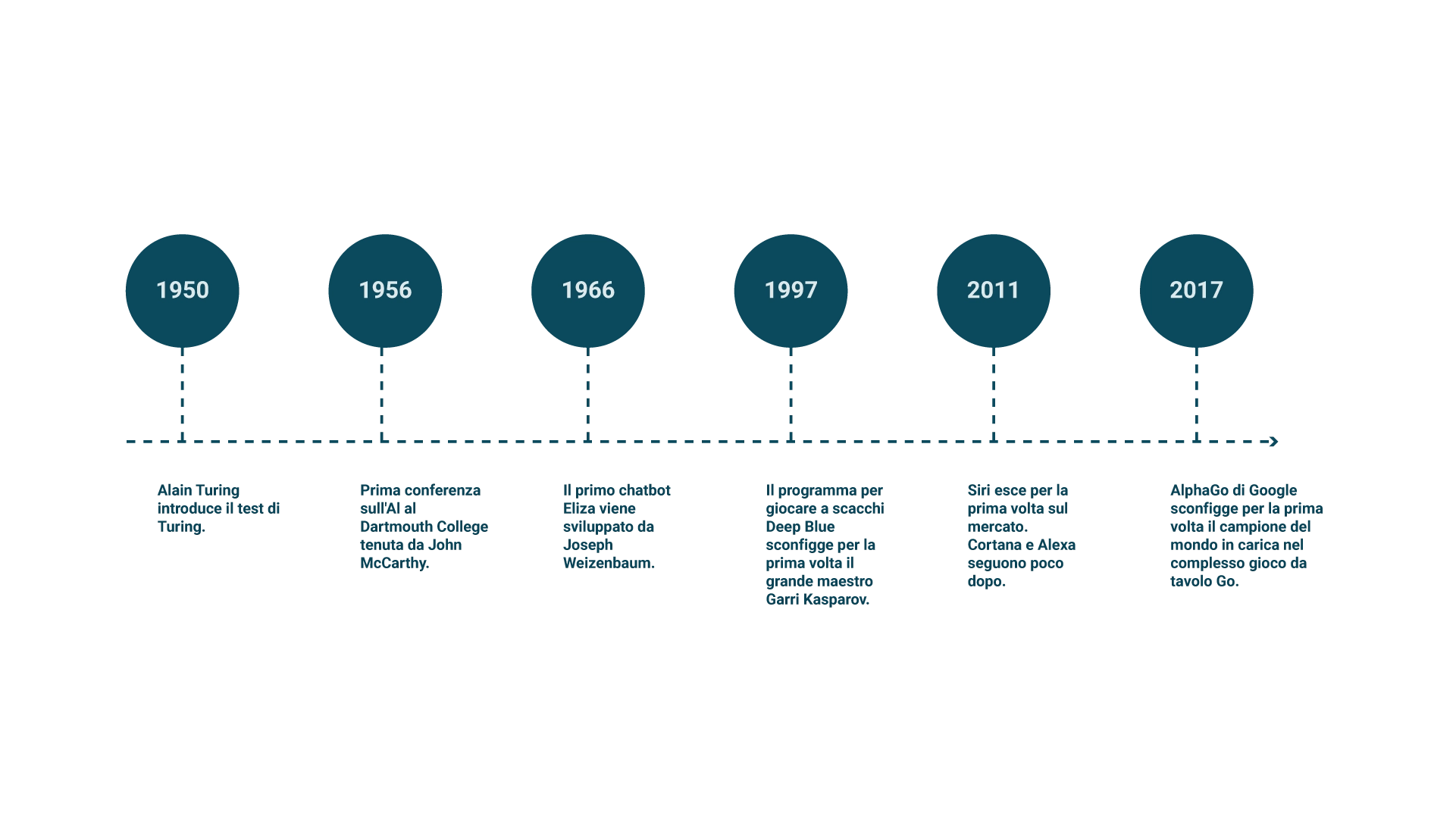
However, starting in the 1970s, AI went through a period of stagnation known as the “AI winter,” due to slowed technological progress, lack of funding, and unmet expectations. AI saw a resurgence in the 1990s with the advent of new learning techniques such as multilayer neural networks and deep learning algorithms. Prominent researchers like Geoffrey Hinton, Yann LeCun, and Yoshua Bengio—known as the “fathers of Deep Learning”—played a pivotal role in this era.
Their contributions, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), revolutionized image recognition and natural language processing. Throughout the 2000s and 2010s, AI progressed rapidly, driven by increased computing power and the availability of large datasets. Breakthroughs such as DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeating the world champion in Go showcased AI’s ability to solve highly complex problems.
Today, AI is embedded in everyday technologies like search engines, virtual assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa), and recommendation platforms (e.g., Netflix, Amazon). It also plays a critical role in sectors like medicine, finance, industry, and transportation
Machine Learning: an approach to AI
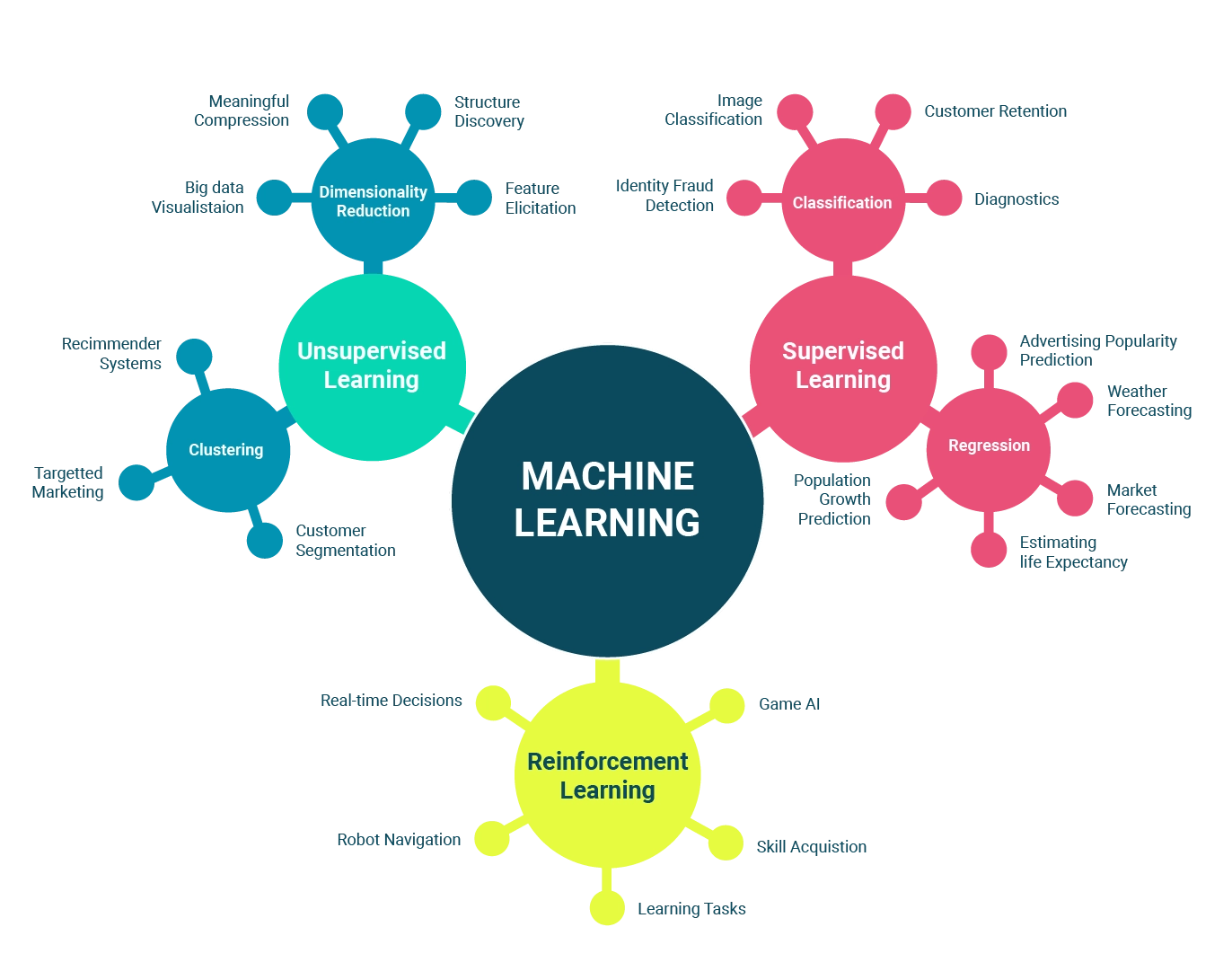
Types of Machine Learning:
- Supervised Learning: The system is trained on labeled data to predict outcomes for new inputs. Examples include:
- Facial recognition (identifying people based on their facial features)
- Medical diagnostics (predicting the presence of diseases based on examinations and patient data)
- Spam detection (identifying unwanted emails based on specific characteristics)
- Unsupervised Learning: The system identifies patterns in unlabeled data. Examples include:
- Market segmentation (identification of consumer groups with similar characteristics to tailor marketing strategies)
- Social network analysis (identification of communities within social networks based on the structure of connections between users)
- Anomaly detection (detection of unusual or suspicious behavior in complex systems such as cybersecurity or predictive maintenance)
- Reinforcement Learning: The system learns by interacting with its environment and receiving feedback. Examples include:
- Robotics (training robots to perform complex tasks, such as controlling a robotic arm or navigating unfamiliar environments)
- Games (e.g., chess, Go) (training intelligent agents to play games such as chess, Go, and video games)
- Energy systems optimization (adjusting energy use and distribution in power grids to maximize energy efficiency)
Practical applications of AI
AI has improved performance and optimized processes across many industries:
- Virtual Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to interact with users intuitively (Hirschberg & Manning, 2015).
- Medicine: AI aids in diagnostics, personalized therapies, and drug discovery. Deep learning matches or exceeds expert accuracy in identifying conditions like skin cancer (Esteva et al., 2017).
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles and intelligent traffic systems improve safety and efficiency (Bishop, 2018).
- Industry: AI-driven automation increases productivity and enables predictive maintenance (Lu et al., 2017).
- Finance: AI enhances trading and risk management by analyzing large data sets (Dixon et al., 2020).
The future of AI
Key Areas of Innovation:
- Natural Language Understanding: Advanced models like OpenAI’s GPT-3 are enhancing communication, sentiment analysis, and translation.
- Computer Vision: Deep learning and CNNs are advancing image recognition and diagnostics.
- Content Generation: Algorithms like GANs produce realistic text, images, and video for use in entertainment and marketing.
Leading Research Centers:
- OpenAI: Focused on safe and beneficial AI.
- DeepMind: Known for AlphaGo and AlphaZero, pioneers in reinforcement learning.
Social and Ethical Impacts of AI
AI must be developed responsibly to benefit everyone:
- Inclusion: Ensuring equitable access to AI technologies.
- Ethical Bias: Preventing AI from perpetuating existing biases.
- Data Protection: Securing user data and maintaining privacy.
AI’s impact on jobs also requires reskilling and adapting education systems.
Conclusion
AI and Machine Learning are transforming the way we live, work, and solve problems. As we continue to advance, it is essential to do so responsibly, keeping ethical and societal impacts at the forefront.
Sources
Crawford, K., & Calo, R. (2016). There is a blind spot in AI research. Nature, 538(7625), 311-313.
O’Neil, C. (2016). Weapons of math destruction. Broadway Books.
Bibliographic References
Bishop, R. (2018). Autonomous vehicles and the law. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Dixon, M., Klabjan, D., & Siolas, G. (2020). Artificial intelligence in finance. Academic Press.
Esteva, A., et al. (2017). Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature.
Lu, Y., et al. (2017). Smart manufacturing systems. Engineering.
Indice
Iscriviti alla newsletter
Indice
Iscriviti alla newsletter
Get more information
Home » What is Artificial Intelligence and why it is useful for businesses