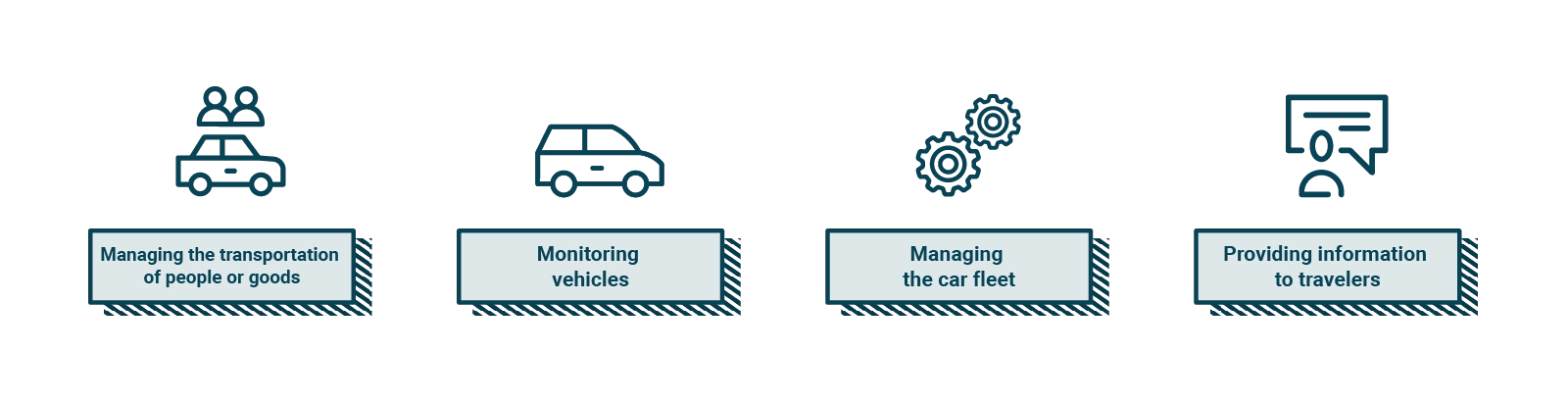
Telematics platforms for mobility can be used in many areas, such as public transport, private or freight transport, vehicle sharing, and fleet management.
A mobility telematics platform can be used to support vehicle sharing, which is the service of sharing the use of a vehicle with other people. There are different types of vehicle sharing services, such as car sharing, bike sharing, or scooter sharing.
In general, telematics mobility platforms can be used to support private transportation (vehicle sharing) in several ways, for example:
A telematics platform for mobility is useful in many ways to support logistics activities for:
Here are some examples of use cases of a telematics mobility platform for public transportation:
A mobility telematics platform can be used in many ways to support fleet management (Fleet Management) for:
Inventory management: the telematics platform can be used to manage stocks of spare parts and accessories for vehicles, for example, to keep track of available quantities or to obtain information on the location of vehicles carrying goods.
The components of a telematics platform for mobility can vary depending on the specific needs of the company or industry in which it is used. In general, however, a telematics platform for mobility can consist of the following components:
Sensors are very important components of smart mobility solutions, as they enable the collection and analysis of real-time data about mobility and the surrounding environment. Here are some ways in which sensors can be used in smart mobility solutions:
Traffic detection: sensors can be used to collect data on traffic congestion to optimize vehicle routes and reduce travel times.
Air quality monitoring: sensors can be used to collect data on air quality to promote the use of sustainable modes of transportation and reduce pollution.
Vehicle detection: sensors can be used to detect the presence of vehicles and collect data on their location in order to optimize fleet management and reduce maintenance costs.
Pedestrian and cyclist detection: sensors can be used to detect the presence of pedestrians and cyclists in order to ensure traffic safety and promote the use of sustainable transportation modes.
In summary, sensors play a key role in smart mobility solutions, as they enable real-time data on mobility and the surrounding environment to be collected and analyzed in order to offer convenient and sustainable mobility solutions to users.
GPS (Global Positioning System) is a very important component of smart mobility solutions, as it allows the geographical location of an object or person to be determined accurately and in real time. Here are some ways in which GPS can be used in smart mobility solutions:
Route planning: GPS can be used to determine the geographic location of vehicles and plan the most efficient routes to reduce travel time and transportation costs.
Fleet management: GPS can be used to monitor the location of vehicles and optimize their management, for example through the use of technologies such as Vehicle Tracking.
On-demand mobility services: GPS can be used to determine the location of vehicles and customers in order to provide on-demand mobility services efficiently and cost-effectively.
Safety monitoring: GPS can be used to monitor the location of vehicles and ensure traffic safety, such as through the use of technologies such as Vehicle Monitoring.
In summary, GPS is a key component of smart mobility solutions, as it allows the geographical location of an object or person to be determined accurately and in real time in order to offer convenient and sustainable mobility solutions to users
Innovation comes from knowledge. big data and smart mobility are two areas that often meet and can benefit from each other. Here are some ways in which big data can be used in smart mobility:
Route planning: big data can be used to collect and analyze data on traffic flows and mobility demand in order to optimize vehicle routes and reduce travel times.
Fleet management: big data can be used to collect and analyze data on vehicle utilization and performance in order to optimize fleet management and reduce maintenance costs.
On-demand mobility services: big data can be used to collect and analyze data on mobility demand in order to provide on-demand mobility services in real time and efficiently.
Demand forecasting: big data can be used to collect and analyze data on mobility demand in order to forecast future needs and adapt mobility services accordingly.
In summary, big data can be used to optimize the use of transportation resources and offer convenient and sustainable mobility solutions to users.
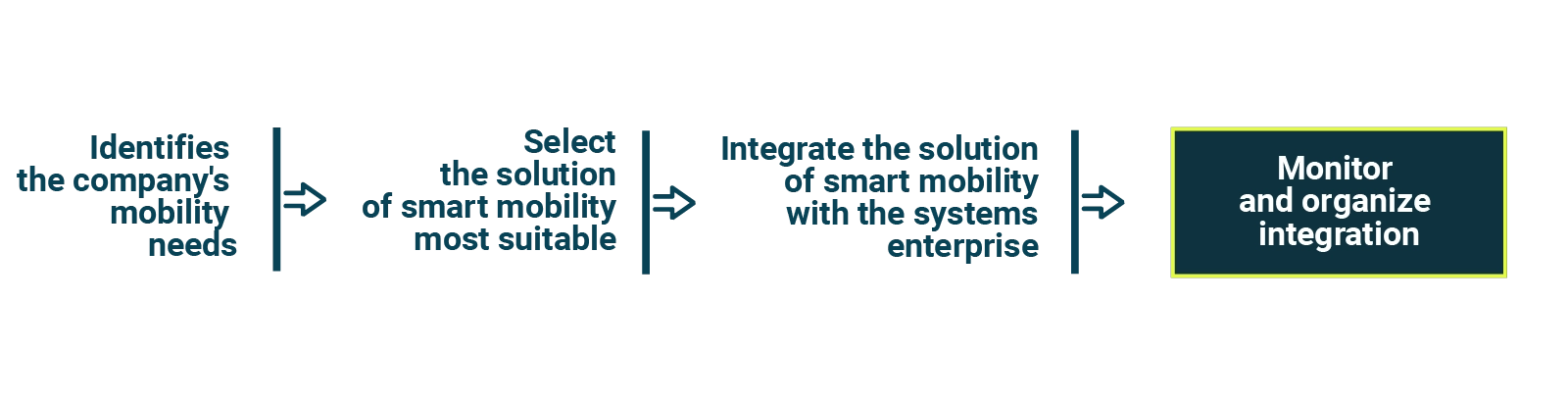
Identify the company's mobility needs: before integrating a smart mobility solution, it is important to identify the company's mobility needs and understand how these can be met efficiently and sustainably.
Select the most suitable smart mobility solution: once the company's mobility needs have been identified, it is important to select the most suitable smart mobility solution, taking into consideration factors such as scalability, flexibility and compatibility with enterprise systems.
Integrate the smart mobility solution with enterprise systems: once the smart mobility solution has been selected, it is important to integrate it with enterprise systems, such as through the use of APIs or integration solutions. This will make it possible to take full advantage of the benefits of smart mobility and achieve greater efficiency in managing transportation resources.
Monitor and optimize the integration: once the smart mobility solution has been integrated with enterprise systems, it is important to monitor the effectiveness of the integration and continuously optimize it, such as through the analysis of collected data and the adoption of automation solutions.
In summary, the integration of a smart mobility solution with enterprise systems is important to fully exploit the benefits of smart mobility and optimize the use of transportation resources.