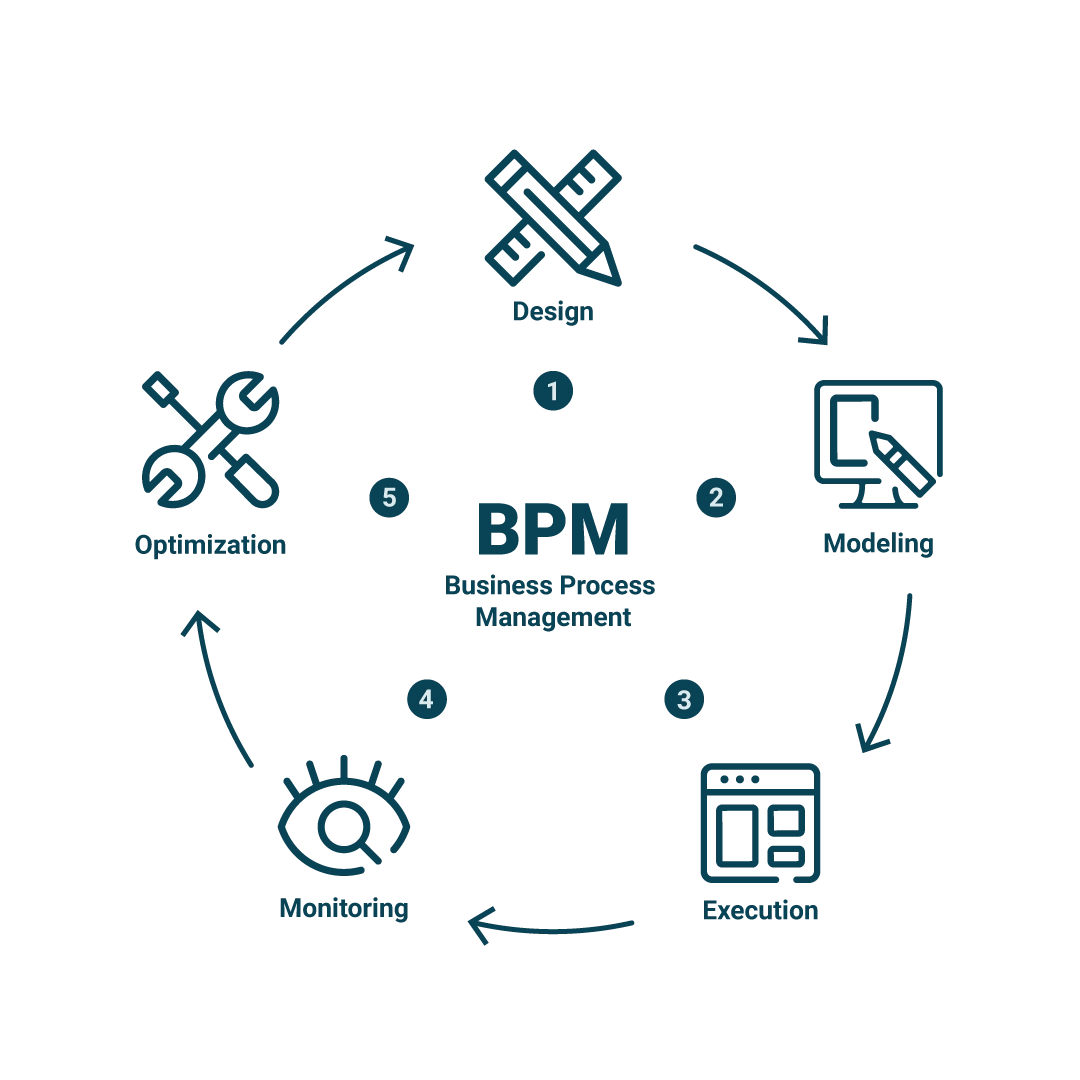
Business Process Management (BPM) is a multifaceted concept that on the one hand refers to business management and on the other to information technology and thus has a direct relationship with Robotic Process Automation.
In fact, since the ultimate goal of BPM is to make business as efficient and effective as possible, RPA could only be a strategic ally.
RPA refers to the ability to outsource certain tasks to software in order to make processes faster. RPA targets tasks that are simple and routine but contribute largely to streamlining operations, allowing human resources to add new value by leveraging their professionalism and expertise in more strategic tasks where human skills find application.
In summary, RPA aims to reduce repetitive and simple rule-based manual activities by shifting tasks that do not require analysis and decision-making to robots.
In this sense, RPA is a valuable ally of BPM, a tool for optimizing time, reducing errors, and using human resources for more strategically relevant processes.
There are three main elements around which ad hoc BPM strategies can be built: integration, people, and documents.
Below we look at the three cases in detail.
The advantages of introducing a BPM solution into the company are many and are reflected on many fronts. Let's look at some of them:
There are areas where BPM software performs best by maximizing processes and resources. Let's look at some of them:
Content distribution: media companies can integrate BPM to automate the entire process from content creation to delivery. They can also optimize traffic and work order tracking.
Customer service: a key example is chatbots. Once key questions are identified these can be handled by chatbots, reducing pressure on the team when a high volume of service requests arise.
Human resources: BPM offers the ability to optimize specific areas such as on and off employees, performance appraisals, vacation requests, and timesheet approval.
Banks: especially useful in processes for evaluating individuals or businesses for loan disbursement, a variety of data collected against certain predefined criteria are analyzed. BPM expedites analysis and decisions on loan eligibility by reducing possible errors.
Order fulfillment: companies can use BPM for order management and fulfillment, automating this process and letting the human resources of can focus on customer care, generating more business value.