Introduction
Smart Mobility is a concept that has become increasingly popular in recent years.
But what exactly does it mean? Smart Mobility refers to intelligent, flexible and sustainable mobility. It is about adapting transportation systems to the contingent needs of citizens, offering customized and environmentally friendly mobility solutions.
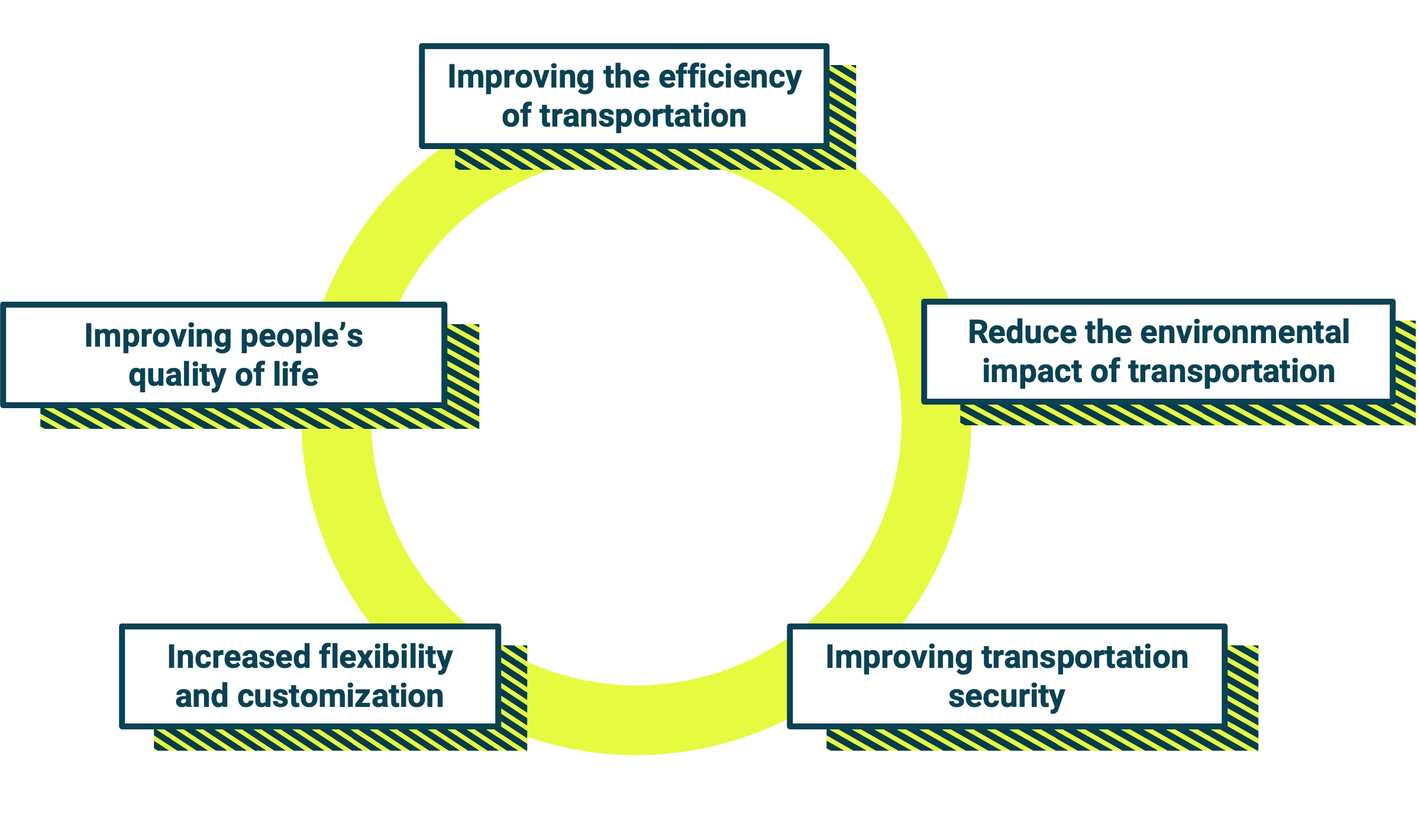
The goal of Smart Mobility is to improve people's quality of life and make cities more livable. Through the use of digital technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), it is possible to optimize the use of transportation resources, reduce pollution, and improve the efficiency of mobility services.
Once upon a time, the streets of our cities were dominated by the noises of internal combustion engines and the hubbub of people hurrying to their destinations. The automobile was the undisputed queen of mobility, a symbol of freedom and independence. But the world was changing, and with it, our conception of travel.
Today we are talking about Smart Mobility, which with its entry, is opening the door to a future of intelligent and sustainable transportation.
Cities, crowded and polluted, needed a revolution, a new way of thinking about mobility, toward a greener, more efficient and more connected future.
The story of Smart Mobility is one of innovation and adaptation. Over the years, we have seen a real transformation of transportation. Streets have filled with electric bicycles and scooters, offering environmentally friendly and economical alternatives to car use. Car sharing and carpooling services have taken hold, allowing people to share trips and reduce their environmental impact.
But Smart Mobility is not just limited to vehicles. It is a complex ecosystem, involving technology, data and infrastructure. With the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), vehicles can communicate with each other and their surroundings, optimizing routes, reducing traffic congestion, and improving road safety.
Cities, in turn, have adapted to accommodate Smart Mobility. Infrastructure has evolved, with the installation of electric vehicle charging stations and the integration of smart traffic management systems. Local governments have promoted the construction of bike lanes and pedestrian sidewalks, creating safe and accessible spaces for micro-mobility vehicles.
But Smart Mobility is not just a matter of technology and infrastructure. It is a matter of cultural change and mindset. People are beginning to reevaluate their relationship with the automobile, choosing more sustainable and conscious mobility solutions. Vehicle sharing and the combined use of different modes of transportation are becoming increasingly common.
This new era of mobility offers numerous benefits. In addition to reducing pollution and environmental impact, Smart Mobility promotes greater efficiency in transportation. Journeys become smoother and faster, thanks to intelligent traffic management and route optimization. Cities are transformed into more livable places, with reduced noise and air pollution.
But the real beauty of Smart Mobility lies in the opportunity to create a more connected and inclusive future.
Thanks to technology, mobility services can be accessible to everyone, regardless of age, ability, or geographic location.
The elderly and people with disabilities can rely on customized solutions that make it easier for them to get around. Rural and remote areas can benefit from efficient and affordable transportation services, improving accessibility and quality of life for residents.
But Smart Mobility is more than just a technological revolution. It is a vision of a sustainable future in which transportation is integrated with environmental protection and people's quality of life. Cities become vibrant green spaces with a balance of vehicles, pedestrians and cyclists. Clean, renewable energy powers transportation, reducing climate impacts and improving the health of communities.
What is Smart Mobility
Sustainable Mobility and Smart Mobility: what future for mobility?
Shifting from a lifestyle based on vehicle ownership, particularly the car, to a lifestyle based on the concept of Mobility-as-a-Service is not easy. In fact, it is necessary to consider mobility as a shared service that offers a great many benefits for the individual citizen, society, and the environment.
Specifically, mobility-as-a-service is a relatively new concept that not only changes the business model for providing transportation services, but also promises a change in the means and mode of service delivery itself.
Thus, this concept was born to be applied especially in large cities, where traffic congestion and levels of air and environmental pollution have reached their peak.
Sustainable mobility is a concept that refers to the use of transportation modes that are environmentally friendly and able to meet people's mobility needs efficiently and equitably. Smart mobility, on the other hand, is an approach that aims to optimize the use of transportation resources through the adoption of advanced technologies and innovative solutions. Here are some things you need to know about the future of smart and sustainable mobility:
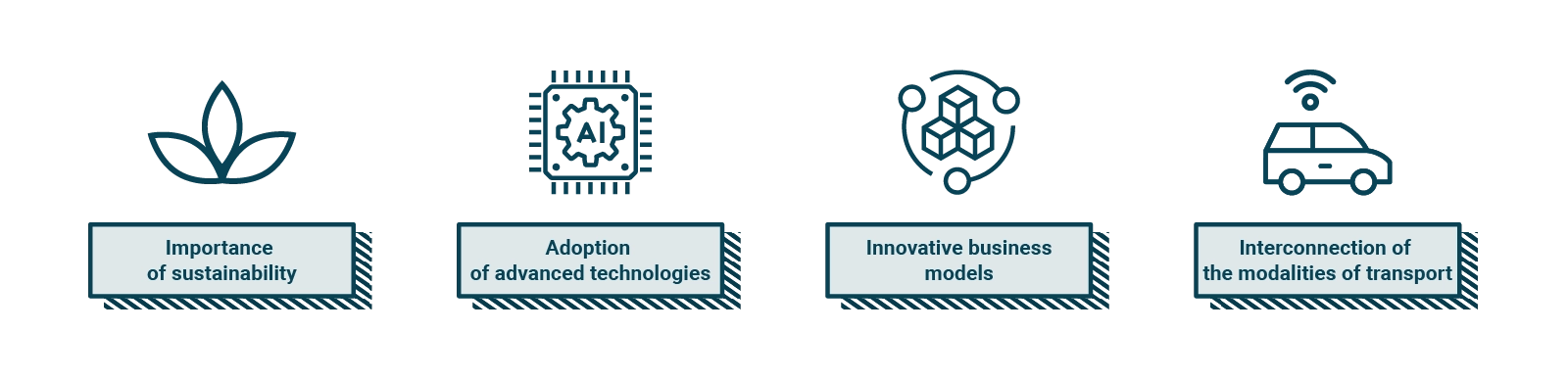
- Importance of sustainability: the future of mobility will increasingly focus on sustainability as there is a growing awareness of the impact of transportation on the environment and human health. In addition, there are more and more policies and initiatives to promote sustainable mobility.
- Adoption of advanced technologies: the future of mobility will see an increasing adoption of advanced technologies, such as self-driving vehicles or telematics platforms for mobility. These technologies will make it possible to optimize the use of transportation resources and provide convenient and sustainable mobility solutions.
- Innovative business models: the future of mobility will also see the emergence of new business models, such as Mobility as a Service (Maas), that enable the shared use of vehicles and infrastructure and offer integrated and personalized mobility solutions.
- Interconnection of transport modes: the future of mobility will see greater interconnection of different transport modes, with the aim of offering users integrated and convenient mobility solutions. For example, it will be possible to use apps to plan routes that combine different modes of transportation, such as public transportation, bike sharing, or car sharing.
How will we move in 10 years?
Smart mobility: how it will change our lives (and our cities)
Our insight

Automazione e Intelligenza Artificiale, i vantaggi per le aziende
L'automazione dei processi aziendali è cruciale per la competitività delle aziende. Ecco come l’IA può aiutarla.
Approfondimento

Mobility as a Service: The Mobility as a Service (MaaS) model
Mobility as a Service (Maas) is a business model that is based on offering mobility services as an all-inclusive solution for users. In other words, Maas offers a variety of transportation options, such as public transportation, car sharing, or bike sharing, in one integrated and customized solution.
Maas relies on the use of advanced technologies, such as telematics mobility platforms, to manage and coordinate different transportation options. The goal of Maas is to offer users a flexible and customized mobility solution that fits their needs and preferences.
Maas can be used in different ways, such as for transporting people or goods. For example, public or private transportation companies can use Maas to offer integrated mobility services to their users, while logistics companies can use Maas to manage the transportation of goods.
Increasingly prevalent in various cities around the world, MaasS will increasingly find its application in our daily lives.
In general, the cities where smart mobility is most present are those where there is a strong demand for sustainable mobility and where there are favorable conditions for the adoption of innovative solutions.
Some of the European cities, where smart mobility is particularly developed are:
Copenhagen: the Danish city is considered an example of smart mobility, as it offers a wide range of sustainable transportation options, such as public transportation, bike sharing, or car sharing.
Amsterdam: the Dutch city is known for its network of bike lanes and its bike-sharing system, which make it easy and convenient to get around by bicycle.
Helsinki: The Finnish city has developed a Maas platform, which offers users an integrated and customized mobility solution that includes public transport, car sharing, and bike sharing.
A virtuous case: Singapore
In Singapore, smart mobility is being applied in a variety of ways. Here are some examples of how smart mobility is being used in Singapore:
Public transportation: in Singapore, public transportation is extensive and reliable, and includes means such as buses, trains, and subways. Smart mobility is used to optimize public transportation, such as through the use of route planning technologies or big data to predict traffic flows.
Car sharing: Singapore has several companies that offer car sharing services, which allow users to share the use of a car with other people. Smart mobility is used to manage these services, such as through the use of apps to reserve and access cars or sensors to monitor vehicle use.
Bike sharing: there are several companies in Singapore that offer bike sharing services, which allow users to share the use of a bicycle with other people. Smart mobility is used to manage these services, such as through the use of apps to reserve and access bikes or sensors to monitor bike use.
Mobility as a Service (Maas): a Maas platform has been developed in Singapore, offering users an integrated and customized mobility solution that includes public transportation, car sharing, and bike sharing. Smart mobility is being used to manage this platform, such as through the use of apps to book and access services or algorithms to optimize routes.
How far are we from this scenario? Do we have the technologies to facilitate this development?
Sustainable mobility: A passing trend or a strategic choice?
According to the best estimates, by 2030, 2 billion people will move to urban centers, where 70 percent of the population will be concentrated: by 2050, the world's urban population is expected to exceed 6 billion. That is why the future lies in sustainable urban development of cities. Not surprisingly, experts agree precisely that the city of the future will be sustainable.
Indeed, all over the world, innovative solutions on the smart city model are being tested. From Saudi Arabia to Japan, from the United States to Singapore, visions of urban centers driven by concepts of sustainability and technological innovation are emerging.
What does this all mean? A sustainable city is inclusive, safe and enduring: it must pay attention to waste management and air control, protect and enhance the landscape and cultural heritage, ensure safe and quality housing and, at the same time, allow citizens access to decisions regarding planning and improvement of the cities themselves.
In Germany, authoritative studies have shown that in a city like Berlin, cars currently account for more than 40 percent of traffic and occupy 80 percent of the space. The rest is divided among buses, trains, bicycles and pedestrians.
This is why we need a more balanced distribution among the different means of transportation and encourage vehicle-sharing policies.
Another important trend to consider in this context is that of digitization, which will play an increasingly crucial role. Ideally, all means of transportation should be integrated and manageable through a single app. The app should allow people to choose their preferred provider through which to book everything from buses to bikes and cars.
How far are we from this scenario? Do we have the technologies to facilitate this development?
Technologies of Smart Mobility
Smart Mobility is based on a series of innovative technologies that make its implementation possible. Let's look at the main ones:
Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT enables the connection between vehicles, road infrastructure, and smart devices, allowing real-time information exchange. Thanks to this technology, it is possible to monitor traffic, collect data, and manage transportation flows more efficiently.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence plays a fundamental role in Smart Mobility. With AI, it is possible to develop route optimization algorithms, assisted driving systems, and advanced traffic management solutions, ensuring greater safety and efficiency in transportation.
Big Data
Big Data management is a key element in Smart Mobility. By collecting and analyzing large amounts of data from sensors, devices, and connected vehicles, detailed information about traffic, travel habits, and user preferences can be obtained. This data can be used to optimize routes, predict traffic flows, and provide personalized services to users.
What are the benefits of adopting a telematics platform for mobility?
Smart Mobility offers a range of benefits that go beyond simply improving mobility. Let's look at the main ones:
- Pollution reduction
Traditional mobility based on fossil fuels is one of the main sources of air pollution. Smart Mobility promotes the adoption of electric, hybrid, and low-emission vehicles, drastically reducing the environmental impact of road transportation.
- Increased energy efficiency
Smart Mobility is based on optimizing traffic flows and intelligent vehicle management. Through the use of advanced algorithms and sensors, it is possible to reduce travel times, avoid traffic congestion, and optimize the use of energy resources.
- Enhanced user experience
Thanks to Smart Mobility, passengers can enjoy more convenient, safe, and efficient transportation services. Intelligent mobility solutions provide real-time information on public transportation schedules, optimized routes, and integrated payment systems, simplifying the lives of commuters.
Adopting a telematics platform for mobility can bring numerous advantages for businesses, such as:
- Improvement of efficiency: Telematics platforms for mobility can help optimize the transportation of people or goods, for example, by planning the optimal route or collecting data on vehicle location.
- Cost reduction: Telematics platforms for mobility can help reduce costs, for example, by monitoring fuel consumption or managing vehicle maintenance.
- Increase in safety: Telematics platforms for mobility can enhance safety, for example, by providing real-time information on vehicle location or speed.
- Enhancement of service quality: Telematics platforms for mobility can contribute to improving the quality of service provided, for example, by providing information to travelers or managing the delivery of goods.
- Increase in transparency: Telematics platforms for mobility can enhance transparency, for example, by providing real-time information on vehicle location or inventory status.
Why People Love Smart Mobility
People love smart mobility for various reasons, such as:

- Convenience: It offers users greater convenience by providing easy and convenient access to a variety of transportation options. For example, mobility apps can be used to book and access services or plan optimal routes.
- Flexibility: It provides users with greater flexibility as they can choose the mode of transportation that best suits their needs and preferences. For instance, users can opt for public transportation, car sharing, or bike sharing based on their requirements.
- Sustainability: Smart mobility offers users increased sustainability by enabling them to reduce the environmental impact of transportation. For example, using low-impact vehicles or car sharing and bike sharing solutions can help reduce pollution and preserve resources.
- Safety: It ensures users greater safety by providing access to secure and reliable transportation services. For instance, the use of advanced technologies like driver assistance systems can help prevent accidents, promote safe driving practices, and minimize driver distractions.
Who Should Adopt Smart Mobility Solutions
People love smart mobility for various reasons, such as:
- Individuals: People who want to benefit from convenient, flexible, sustainable, and safe transportation options can adopt smart mobility solutions.
- Businesses: Companies involved in transportation, logistics, or delivery services can adopt smart mobility solutions to enhance their operations, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and provide better services to their customers.
- Cities and Municipalities: Local governments can adopt smart mobility solutions to optimize transportation systems, reduce congestion, minimize environmental impact, and enhance the overall quality of life for residents.
- Transportation Service Providers: Public transportation agencies, ride-sharing companies, and other transportation service providers can adopt smart mobility solutions to modernize their offerings, improve customer experience, and optimize their operations.
- Technology Providers: Companies specializing in mobility technologies can develop and offer smart mobility solutions to various stakeholders, enabling them to benefit from the advantages of advanced transportation systems.
What are the environmental benefits of adopting Smart Mobility solutions?
Adopting smart mobility solutions can have several advantages for the environment, such as:
- Pollution Reduction: Smart mobility solutions can help reduce pollution by promoting the use of low-impact vehicles and sustainable modes of transportation like public transport or bike sharing.
- Resource Savings: These solutions can contribute to resource savings by optimizing transportation through advanced technologies and business models like Mobility as a Service (MaaS), which allows for vehicle and infrastructure sharing.
- Traffic Reduction: Smart mobility solutions can help reduce traffic congestion by promoting sustainable modes of transportation and implementing advanced technologies to optimize traffic management.
Challenges of Smart Mobility
Despite the numerous advantages, Smart Mobility also faces some challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its long-term success.
Infrastructure and Interoperability:
The transition to Smart Mobility requires suitable and interoperable infrastructure. It is necessary to develop charging networks for electric vehicles, traffic management sensors, and advanced communication systems that can support the interconnection of various stakeholders.
On the path to Smart Mobility, one of the fundamental challenges is adapting infrastructure and ensuring system interoperability. To achieve intelligent and sustainable mobility, investment in appropriate infrastructure is necessary, along with ensuring effective communication among the various stakeholders involved.
Let's start with infrastructure. To support the transition to greener vehicles like electric ones, it is essential to develop a widespread and accessible charging network. Charging stations should be strategically positioned in cities, along roads, and in parking areas to ensure efficient and convenient coverage for users. This requires commitment from both the public and private sectors to facilitate and make the transition to electric vehicles convenient for everyone.
However, Smart Mobility goes beyond just vehicle charging. It also requires investment in sensors and advanced technologies for traffic management. Implementing intelligent sensors can help collect real-time data on road conditions, traffic flow, and driver preferences. This information can be used to optimize traffic management by identifying congestion areas and providing guidance to drivers to reduce travel times and improve traffic flow.
But the key to Smart Mobility lies in system interoperability. It means that different platforms and technologies should be able to communicate with each other harmoniously and seamlessly. For example, data collected by sensors can be used by traffic management systems and route planning applications, enabling consistent and accurate information flow.
This requires the establishment of common standards and the adoption of open communication protocols so that the various stakeholders of Smart Mobility can collaborate effectively.
Interoperability not only applies to communication between infrastructures but also to the integration of different mobility services. This means that various stakeholders, such as car-sharing providers, public transport operators, and digital mobility platforms, should be able to collaborate and share data to offer a comprehensive and integrated solution to citizens. This requires an open and collaborative approach where the common interest is to provide quality services and facilitate people's movement.
In summary, the transition to Smart Mobility requires investment in appropriate infrastructure, from electric vehicle charging networks to intelligent sensors for traffic management. However, it is not enough. Ensuring system interoperability is crucial so that different technologies and platforms can effectively communicate with each other. This entails adopting common standards and open communication protocols, allowing synergy among the various stakeholders involved in Smart Mobility.
Interoperability of infrastructures and systems offers numerous benefits. It enables more efficient traffic management, reducing road congestion and improving transport flow. Additionally, it facilitates resource optimization by allowing better route planning and reducing energy waste.
However, interoperability is not just a technological matter. It is an approach aimed at creating an integrated network of mobility services where citizens can benefit from personalized and convenient solutions. Through data sharing and collaboration among different stakeholders, it is possible to offer a seamless mobility experience, combining various modes of transport into a single optimized journey.
Imagine being able to plan your trip using an application that integrates real-time information on public transport, car-sharing services, electric bicycles, and even micro-mobility options like scooters. You could choose the most convenient and sustainable solution, receiving precise and up-to-date directions for your route.
The interoperability of infrastructures and systems is the key to realizing this vision of smart mobility. It is an ongoing process as new technologies and services are constantly introduced. The important thing is to maintain an open and collaborative mindset, enabling continuous growth and innovation in the Smart Mobility sector.
Regulation and standards:
To fully unleash the potential of Smart Mobility, addressing the issues of regulation and norms is necessary. Current laws and policies must be reviewed and updated to adapt to new technologies and emerging mobility models. It is crucial to define clear rules and common standards to ensure the safety, privacy, and efficiency of intelligent transport systems.
Regulation plays a crucial role in ensuring a safe and reliable environment for Smart Mobility. With the advent of technologies like autonomous driving and vehicle communication, it is necessary to establish rules and protocols to ensure road safety and minimize risks associated with the use of these innovative technologies. Laws should cover aspects such as certification of autonomous vehicles, legal liability in case of accidents, and protection of personal data.
At the same time, privacy is a fundamental factor in Smart Mobility. With the increasing amount of data collected and shared by intelligent vehicles and mobility systems, it is crucial to ensure that personal information is adequately protected. Privacy regulations need to be clear and stringent, allowing individuals to have control over their data and ensuring responsible and compliant usage according to applicable laws.
Furthermore, the efficiency of intelligent transport systems also relies on collaboration and standardization of norms. Establishing common standards for communication and interoperability of devices and mobility services is essential. This would enable better integration among various industry stakeholders and facilitate the exchange of information among vehicles, infrastructures, and digital platforms. Standardizing communication protocols and data formats would promote interoperability and synergy among systems, creating a seamless mobility experience for users.
Conclusion
Smart Mobility represents a unique opportunity to transform the transportation sector, improving sustainability, efficiency, and user experience. By leveraging advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and Big Data, it is possible to create an intelligent and connected transport ecosystem.
However, addressing the challenges related to infrastructure, interoperability, and regulation is crucial for the success of Smart Mobility. Only through collaboration between the public and private sectors, the implementation of appropriate policies, and the promotion of sustainable solutions, can we achieve a future of intelligent mobility.






