How Chat GPT Works – Behind the Scenes
Innovation
Technology
Consulting
Home » Chat GPT – Behind the Scenes
Introduction
Are you curious about how ChatGPT works under the hood? Have you heard about this revolutionary artificial intelligence that’s transforming online interaction? In this article, we reveal the technical foundations of ChatGPT—the virtual assistant powered by a Large Language Model (LLM) and refined through Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF).
This guide compiles months of testing and study into a tool that, along with other developments in LLMs, is set to reshape the future of work.
ChatGPT was launched on November 30, 2022, astonishing the world with its rapid growth. In just two months, it reached 100 million monthly active users—faster than Instagram, which took 30 months. This makes it the fastest-growing app in history. But what powers this success? Let’s find out.

At the heart of ChatGPT is a Large Language Model, specifically GPT-3.5. This deep learning model is trained on massive amounts of text data to understand and generate human language. GPT-3.5 includes 175 billion parameters spread across 96 neural layers, making it one of the most complex AI models ever developed.

Tokens—numerical representations of words or parts of words—are used to process input and generate output efficiently. GPT-3.5 was trained on a dataset containing 500 billion tokens, allowing it to generate structured, grammatically correct, and semantically coherent text.
However, without appropriate safeguards, the model can produce inaccurate or harmful content. This is where RLHF comes in.
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
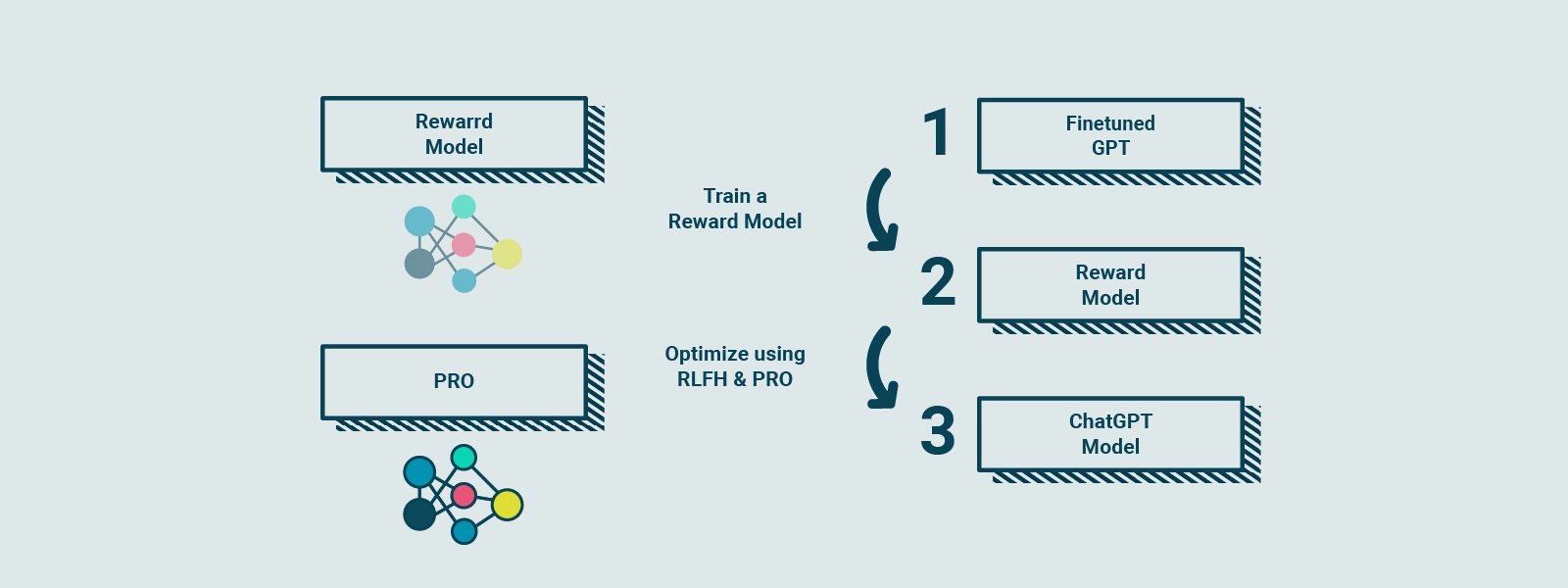
RLHF enhances ChatGPT’s reliability by incorporating human feedback. Real people provide evaluations that form a “reward model,” guiding the AI toward desirable behaviors. Using a technique called Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), the model is trained to improve its responses based on the reward model.
This method helps the model become more aligned with human expectations and values, making interactions more natural and safe.
A brief history of LLMs
Understanding ChatGPT also means understanding the history and function of LLMs. These models use neural networks to learn statistical patterns in language, breaking down input into tokens to process it more effectively.
GPT-3.5, with its immense size and training on diverse web texts, exemplifies the state-of-the-art in this field. However, LLMs still require fine-tuning, such as RLHF, to avoid outputting biased or misleading content.
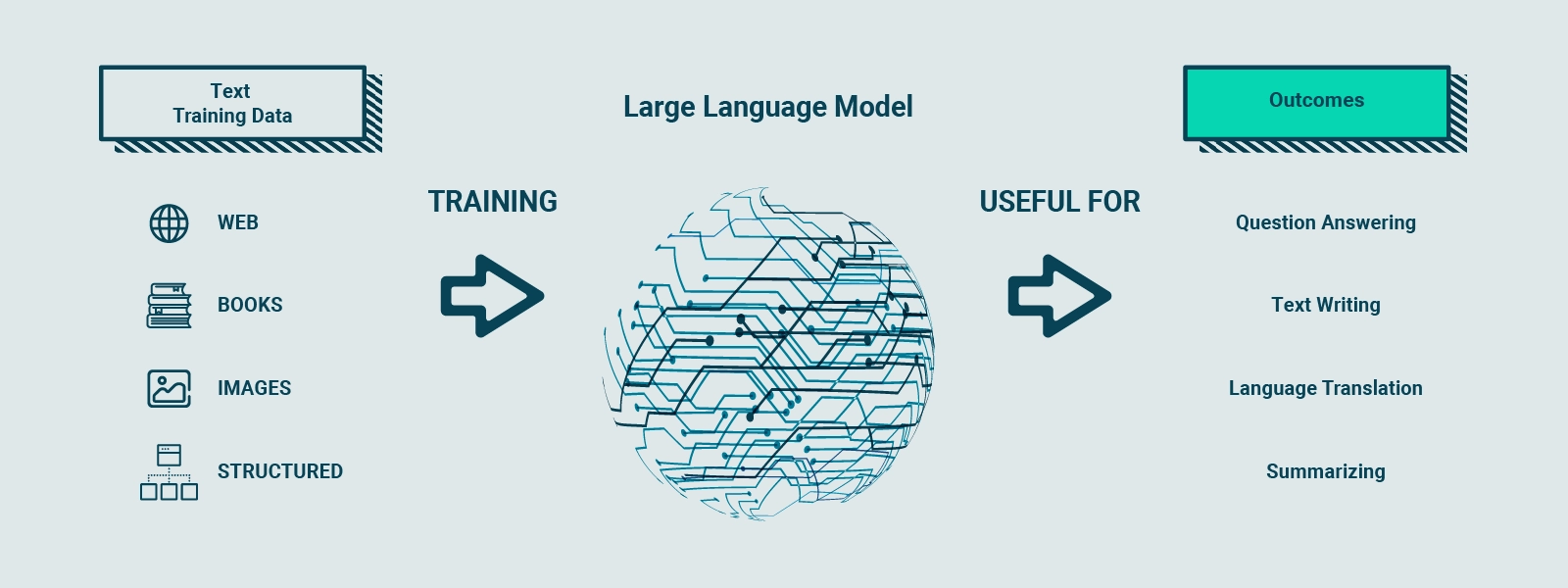
In summary, Large Language Models (LLMs) represent a milestone in artificial intelligence and natural language generation. Their complexity, size, and ability to learn from textual data make them powerful tools for understanding and generating human language accurately. CHAT GPT, based on GPT-3.5, is an excellent example of how LLMs can be applied to create intelligent, high-performance virtual assistants.
How CHAT GPT Works
At the heart of CHAT GPT is the Large Language Model (LLM) GPT-3.5, which is currently used in the application. However, it is important to note that CHAT GPT could also benefit from the use of the newer GPT-4 model, although not much technical information about it is currently available.
GPT-3.5 underwent an intensive training process on a vast amount of Internet data. The source dataset used for training contains an incredible 500 billion tokens, which corresponds to hundreds of billions of words. During training, the model was exposed to a wide range of texts from different online sources.
The main goal of training GPT-3.5 was to teach the model to predict the next token based on a sequence of input tokens. This approach allows GPT-3.5 to generate text that is structured in a grammatically correct and semantically consistent manner with respect to the Internet data on which it was trained.
It is important to note that although GPT-3.5 can generate quality text, it is critical to provide the model with adequate guidance to avoid generating content that is untruthful, toxic, or reflects harmful sentiments.
Further refinement of the model through techniques such as Reinforcement Training from Human Feedback (RLHF) helps to improve the quality and confidence of responses generated by Chat GPT.
Reinforcement Training from Human Feedback
To make the CHAT GPT model more secure, able to provide contextual responses and interact in the style of a virtual assistant, a process called Reinforcement Training from Human Feedback (RLHF) is used. This further training process transforms the basic model into a refined model that better meets user needs and aligns with human values.
RLHF involves collecting feedback from real people to create a “reward model” based on user preferences. This reward model serves as a guide for the model during training. It is similar to a cook practicing the preparation of dishes, following a reward model based on customers’ taste. The cook compares the current dish with a slightly different version and learns which version is better according to the reward model. This process is repeated several times, allowing the cook to hone his cooking skills based on updated customer feedback.

Similarly, GPT-3.5 is subjected to RLHF, collecting feedback from people to create a reward model based on their preferences. Using a technique called Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), the model is trained to improve its performance relative to the reward model. This technique is similar to the cook comparing his current dish with a slightly different variant and learning which version is better according to the reward model. With each iteration, the model gets closer and closer to the users’ preferences, generating better and more personalized responses to requests.
Through RLHF and the use of PPO, GPT-3.5 is being iteratively refined, improving its language generation abilities and adapting to the needs of users. This enables CHAT GPT to generate more accurate, consistent and relevant responses to user questions, creating a more engaging and satisfying interaction experience.
Training an LLM explained simple
OpenAI explained how it ran RLHF on the model, but it is not easy to understand for people not familiar with Machine Learning. Let’s try to understand it with a simple analogy.
Suppose GPT-3.5 is a highly skilled chef who can prepare a wide variety of dishes.
Refining the model of GPT-3.5 with RLHF is like honing this chef’s skills to make the most delicious dishes for his particular customers.
Initially, the chef is trained in the traditional way with a large data set of recipes and cooking techniques.
However, sometimes the chef does not know which dish to prepare for a specific customer request.
To help with this, we collect feedback from real people to create a new dataset (new recipes or variations of previous ones).
By the way, don’t ask for cream in carbonara or pineapple on pizza.
The first step is to create a comparison dataset. We ask the chef to prepare multiple dishes for a given request, and then have the dishes ranked according to taste and presentation.
This helps the chef understand which dishes are preferred by customers.
The next step is reward modeling: the chef uses this feedback to create a “reward model,” which is like a guide to understanding customer preferences.
The higher the reward, the better the dish.
To better understand, let us imagine that the chef is practicing the preparation of dishes following a reward guide.
It is as if the chef compares the dish he just cooked with a slightly different version and learns which dish is better, according to the reward guide.
This process is repeated many times, with the chef honing his skills based on updated feedback from customers.
Each time he repeats the process, the chef gets better and better at preparing dishes that meet customers’ preferences.
A similar concept applies to GPT-3.5, which is refined with RLHF by collecting people’s feedback, creating a reward guide based on their preferences, and then gradually improving the performance of the model using PPO.
PPO – Proximal Policy Optimization
The goal of PPO is to refine the decision policies of machine learning models, enabling them to learn from training data more efficiently. This is accomplished through a series of iterations, in which the model performs actions and compares the results with a slightly modified version of the decision policies. The algorithm evaluates the differences between the two policies and, based on those differences, updates the existing policies to bring the results closer to the desired performance.
PPO is distinguished by its ability to balance the exploration of new strategies with the use of information already learned from the model. This approach allows for better stability in training and greater efficiency in achieving optimal results. In addition, PPO offers advantages in terms of controlling changes made to decision policies, ensuring that changes are moderate and gradual, thus avoiding instability in learning and the occurrence of undesirable effects.
Conclusion
Indice
Iscriviti alla newsletter
Indice
Iscriviti alla newsletter
Get more information
Home » Chat GPT – Behind the Scenes